Struggling with focus or motivation? Dopamine, your brain’s feel-good chemical, plays a big role in regulating mood, focus, and rewards. However, it can become unbalanced from too much stimulation or neglect. This guide will show you simple, natural ways to optimize dopamine for clearer thinking and better productivity.
What Is Dopamine?
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that influences your drive, focus, and pleasure when you pursue goals, eat, or enjoy rewards. When dopamine levels are too high (due to excessive scrolling) or too low (due to boredom), it can disrupt motivation, causing distractions or sluggishness. Balancing dopamine naturally can keep you energized and focused without burnout.

Step-by-Step Protocol to Regulate Dopamine
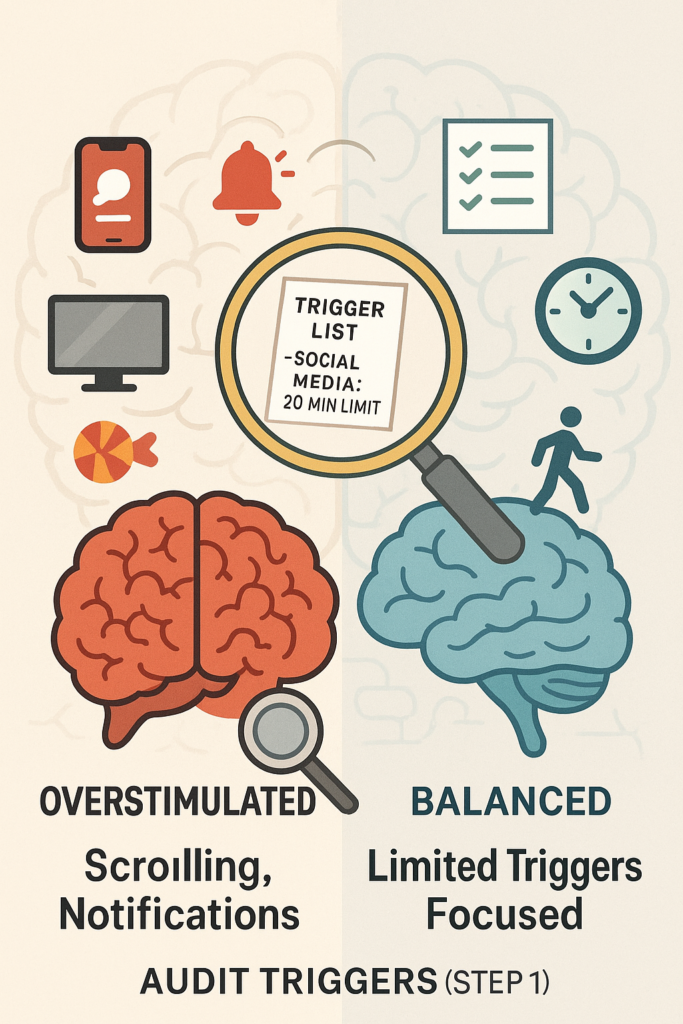
Step 1: Audit Your Dopamine Triggers
Constant notifications and binge-watching can send dopamine levels soaring, making simple tasks feel boring.
How: For one day, track what grabs your attention (e.g., social media, snacks, TV). Pick one high-dopamine habit (e.g., scrolling) and limit it to 20 minutes a day using your phone’s app timer.
Why: Reducing overstimulation helps preserve dopamine for more meaningful tasks.
Step 2: Start Your Day with a Positive Routine
A consistent morning routine helps create small dopamine boosts, setting a productive tone for the day.
How: Spend 10-20 minutes in the morning doing calming activities like stretching, meditation, or planning your day. Avoid screens to keep dopamine levels steady.
Why: Morning habits prime your brain for focus and productivity.
Step 3: Swap Quick Hits for Healthy Rewards
Quick-dopamine activities like gaming or junk food can cause crashes, leaving you feeling unmotivated.
How: Replace one habit (e.g., scrolling) with a healthier reward (e.g., a 5-minute walk, or listening to your favorite song). Reward completing tasks with small wins (e.g., music).
Why: Healthy rewards give a steady stream of dopamine without desensitizing your brain.
Step 4: Fuel Dopamine with Food
Dopamine is made from the amino acid tyrosine, found in protein-rich foods. Poor diet can starve your reward system.
How: Include a tyrosine-rich meal (e.g., eggs, chicken, almonds, bananas) with complex carbs (e.g., oats, quinoa) for better absorption. Avoid sugary snacks to prevent crashes.
Why: Tyrosine supports dopamine production and helps maintain focus.
Step 5: Move Your Body Daily (No Gym Required)
Exercise boosts dopamine by activating reward pathways, while inactivity can dull motivation.
How: Aim for 15-20 minutes of light movement (e.g., walking, dancing). Walking alone releases 85% of the dopamine as running does. Focus on consistency, not intensity.
Why: Physical activity boosts dopamine receptors, improving both mood and focus.
Step 6: Practice Focused Work Blocks
Multitasking or procrastination wastes dopamine without getting results.
How: Use a 25-minute Pomodoro timer for focused work on one task. Turn off notifications and reward yourself with a short break (e.g., stretch, drink tea).
Why: Completing tasks triggers dopamine, reinforcing productivity.
Step 7: Get Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep decreases dopamine receptor sensitivity, making motivation harder to maintain.
How: Get 7-9 hours of sleep each night, followed by a calming bedtime routine (e.g., reading, avoiding screens). Keep your bedroom dark and cool.
Why: Sleep recharges your brain and boosts dopamine sensitivity.
Sample Dopamine Protocol
- Note one high-dopamine habit and limit it to 20 minutes.
- Spend 10–20 minutes on a morning routine (stretch, meditate).
- Swap scrolling for a 5-minute walk or music.
- Eat eggs, chicken, or almonds with carbs daily.
- Move 15–20 minutes (walk, dance, yoga).
- Focus on one task for 25 minutes with a timer.
- Sleep 7–9 hours in a dark, cool room.
Conclusion
Balancing dopamine fuels focus and motivation without the crash of chasing highs. These seven steps—cutting triggers, building habits, and prioritizing sleep—keep you sharp and driven. A tool like a focus timer app (e.g., Focus@Will) can help you stay on track, letting your brain thrive.
References for Further Reading
- Neuroscience: Dopamine’s role in reward and motivation.
- Frontiers in Psychology: Mindfulness and dopamine regulation.
- Journal of Nutrition: Tyrosine’s impact on dopamine synthesis.
- Nature Reviews Neuroscience: Exercise and neurotransmitter balance.